The fight against tuberculosis (TB) in India is at a critical juncture. Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s ambitious goal to eliminate TB by 2025 faces hurdles. Recent developments highlight a disconnect between technological advancements and their implementation in public health programmes.
AI Tools Developed for TB Screening
Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Process
The HTAIn committee evaluates new technologies for cost-effectiveness and efficacy. However, the Central TB Division (CTD) has delayed the introduction of approved AI tools into the national programme. Although both qXR and Genki received positive assessments, they remain unutilised. This contrasts with the CTD’s recommendation for another AI tool, DeepCXR, which lacks a formal HTA assessment.
Implementation Challenges
Despite the availability of effective AI tools, the CTD’s slow response is alarming. The DeepCXR tool, although approved for use, is not widely communicated to state health departments. This lack of clarity hampers the timely integration of AI solutions into TB screening efforts.
Cost-Effectiveness of AI Solutions
Both qXR and Genki have been found to be cost-effective. The cost per case for qXR is ₹30, while Genki costs ₹22. These figures suggest that implementing these tools could lead to savings in TB detection efforts.
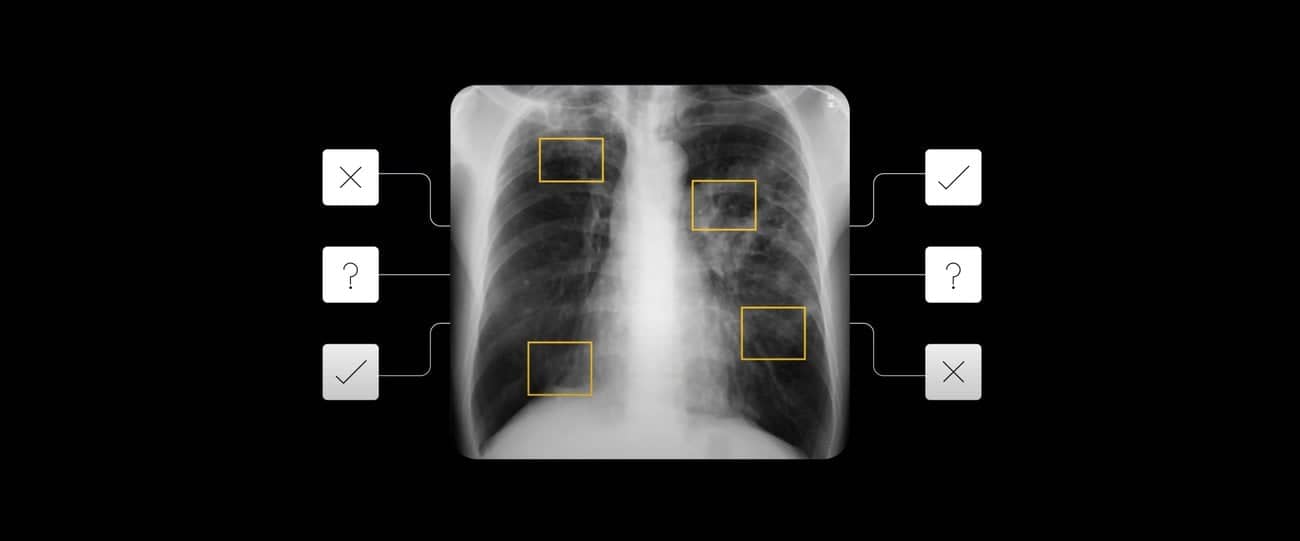
Importance of Chest X-rays in TB Detection
Chest X-rays are crucial in identifying presumptive and subclinical TB cases. They have proven effective in various surveys, detecting a large portion of TB cases. AI-assisted interpretation enhances the speed and accuracy of this process, making it suitable for resource-limited settings.
Leave a Reply