The health of tea plantation workers in Assam has come under scrutiny due to a recent study denoting risk of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA). This life-threatening fungal infection primarily affects tuberculosis (TB) survivors. The research was conducted by a team from Assam Medical College and Hospital, revealing alarming prevalence rates among tea workers.
Context of Tuberculosis in Assam
Tuberculosis remains a critical public health concern in Assam. The National Tuberculosis Prevalence Survey (2019-2021) reported a TB incidence of 217 cases per 100,000 population. Contributing factors include poverty, malnutrition, and poor living conditions. These factors create an environment conducive to the spread of TB and its complications.
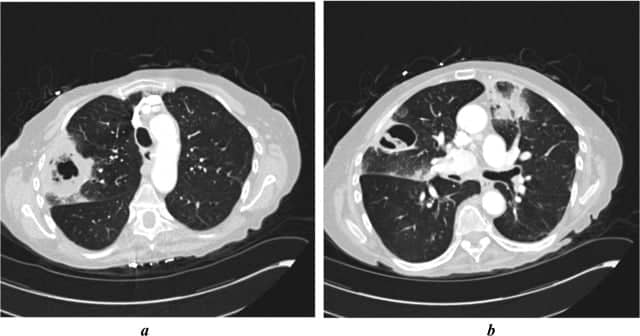
About Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis
Study Findings and Prevalence Rates
Demographics and Risk Factors
The mean age of patients was 41.9 years, with a higher incidence in middle-aged males. Smoking was identified as a potential risk factor. Interestingly, a study in Kenya showed a higher prevalence of CPA in non-smokers, indicating that more research is needed to understand the disease’s risk factors.
Global Comparisons and Health Implications
Assam’s CPA prevalence of 60 cases per 100,000 people exceeds the global average of 42. This situation is worse than in several African countries. The high rates of respiratory illnesses among tea workers contribute to lower productivity and increased medical expenses, leading to economic strain on families.
Leave a Reply